The Revista de Gastroenterología de México (RGM), founded in 1935, is one of the most influential journals of scientific dissemination in Mexico and Latin America. The aim of the present review was to characterize the RGM’s most frequently cited original articles, review articles, and consensuses.
MethodsThe most cited original articles, review articles, and consensuses of the RGM were identified using the Scopus, PubMed, and Google Scholar databases. Their designs and topics, as well as their authors and participating institutions, were analyzed.
ResultsThe most highly cited articles of the RGM corresponded to the period from 1996 to 2018, with a mean of 16.5 citations per article. Fifty-eight percent (n = 29) of the articles belonged to the area of gastroenterology and 20% (n = 10) to surgery. The most frequent topics were functional gastrointestinal disorders, hepatitis virus, and gastric cancer. Thirty-six percent of the articles had a nonrandomized prospective design, followed by cross-sectional studies (26%) and randomized prospective studies (18%).
ConclusionThe 50 most-cited articles included a total of 826 citations and the 10 most-cited consensuses and review articles had a total of 208 citations.
Those studies encompass a diversity of disciplines related to gastroenterology that have impacted the scientific community and correspond to the work of different active research groups in Mexico and other countries.
La Revista de Gastroenterología de México (RGM) fundada en 1935 es una de las revistas de divulgación científica en México y Latinoamérica con mayor impacto. El objetivo del presente estudio es caracterizar los artículos más citados de la RGM incluyendo originales, revisión y consensos.
MétodosSe utilizaron las bases de datos de Scopus, PubMed y Google Scholar para identificar los artículos originales, revisión y consensos más citados de la RGM. Se analizaron sus características como diseño y tema, así como autores e instituciones participantes.
ResultadosLos artículos más citados de la RGM corresponden al periodo entre 1996 y 2018, teniendo un promedio de 16.5 citas por artículo. El 58% (n = 29) de los trabajos pertenecen al área de gastroenterología y 20% (n = 10) a cirugía; los temas más frecuentes fueron: trastorno funcional digestivo, virus de hepatitis y cáncer gástrico. El 36% de los trabajos corresponden a un diseño prospectivo no aleatorizado, seguido de estudios transversales en el 26% y prospectivos aleatorizados en el 18%.
ConclusiónLos 50 artículos más citados representan un total de 826 citas, mientras que los 10 consensos y artículos de revisión más citados, 208 citas.
Estos trabajos presentan una diversidad en disciplinas afines a la gastroenterología que han logrado impactar en la comunidad científica y representan diferentes grupos de investigación activos a lo largo de la república mexicana y otros países.
The Revista de Gastroenterología de México (RGM) is the official publication of the Asociación Mexicana de Gastroenterología, founded in 1935 by Dr. Abraham Ayala González, under the former name Revista de Gastro-Enterología. It is one of the most prestigious journals of scientific dissemination in Mexico and Latin America, with more than 2,700 articles published since its founding and an average of 77 articles annually.1,2
From the beginning of its publication, the RGM has been a space belonging to the entire medical community, both in Mexico and abroad, for the publication of works regarding the clinical and surgical practice related to the digestive tract, as well as for providing relevant and up-to-date information on the specialty of gastroenterology. The journal is published every three months and consists of peer-reviewed works that include original articles, scientific letters, clinical images, brief communications, and letters to the editors. It also publishes review articles, clinical guidelines, and consensuses that are requested by the editorial committee.3 According to the final metrics of 2018, the RGM was characterized as an open access journal with a Source Normalized Impact per Paper (SNIP) of 0.505 and a Hirsch index (H) of 18, putting it in 94th place, from a total of 131 international gastroenterology journals,4 and in 3rd place in Latin America.5
In recent years, works have been published that have examined the most-cited articles in the diverse medical and surgical specialties of oncology,6 cardiology,7 anesthesiology,8 general surgery,9 and urology,10 utilizing bibliometric principles. Bibliometrics is a field of scientific and technologic study for constructing research indicators. The analysis of citations is one of its main methodologies, which arose from the need to objectively measure scientific activity.11,12 Even though there is no perfect method, citation analysis enables the impact of a research study to be evaluated, within the advances of a given scientific discipline, through the number of times an article is cited.13,14 To that end, the Web of Science (Thomson Reuters), Google Scholar (Google Inc.), Scopus (Elsevier), and PubMed (National Library of Medicine) databases are the most widely used in bibliometric studies, each one with certain characteristics, such as multidisciplinary coverage, number of indexed journals, updating frequency, type of access, and time period of the articles.15
The aim of the present study was to identify and characterize the most frequently cited original articles, review articles, and consensuses published in the RGM, to have an accurate overview of the impact the journal has had on the area of gastroenterology.
MethodsThe most frequently cited original articles, review articles, and consensuses published in the RGM were determined, utilizing Elsevier’s Scopus database, and the data obtained from the PubMed and Google Scholar databases were then compared. The search for the works and their hierarchical classification were based on the results obtained from Scopus, given that it is the database that includes the highest number of indexed journals and the lowest number of duplicate citations. When articles had the same number of citations in the Scopus database, the number of citations in the PubMed and Google Scholar databases was utilized for their hierarchical classification.
The search was carried out in May 2020 and encompassed the original articles published from 1949 to 1974 and from 1974 to 2020, to include the years covered by the Scopus database. The articles were categorized in descending order, according to the number of citations, registering the titles and abstracts of the 50 most cited original articles, for their thorough review.
In addition to the number of citations, the following data for each article were obtained: year of publication, authors, participating institutions, country of origin, study design (prospective, retrospective, cross-sectional, meta-analysis, and case series), level of evidence (Oxford Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine), area of study (gastroenterology, endoscopy, surgery, hepatology, and pediatrics), and topic of study.
Finally, an analysis of the most widely read articles on the RGM website was carried out, using alternative metrics to have an overview of reader interaction with the different digital contents, including the number of times an article has been viewed (on PDF, HTML, and EPUB formats), usage (a way to signal if anyone is reading the article or otherwise using the research), captures (indicates that someone wants to come back to the work), and social media (indicates the activity on social media related to the research).
ResultsThe initial search on the Scopus database produced 2,814 works published in the RGM within the study time frame, with a total of 3,863 citations. The 50 most-cited articles (Table 1) accounted for 826 (21%) of the total number of citations. Each article had a minimum of 10 citations and a mean of 16.5 citations per article. Three articles had more than 30 citations, 10 articles had more than 20 citations, and the remaining articles had 10 or more citations.
The 50 most-cited original articles in Spanish or English published in the Revista de Gastroenterología de México.
| Lead author | Year | Title | No. of citations | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | PM | GS | ||||
| 1 | Franklin et al.16 | 2004 | Laparoscopic right hemicolectomy for cancer: 11-year experience | 39 | 16 | 46 |
| 2 | Zablah et al.17 | 2015 | Prevalence of functional gastrointestinal disorders in school-aged children in El Salvador | 34 | 5 | 44 |
| 3 | Hernández-Aranda et al.18 | 1997 | Desnutrición y nutrición parenteral total: estudio de una cohorte para determinar la incidencia del síndrome de realimentación | 33 | 6 | 46 |
| 4 | Rodríguez-García et al.19 | 1999 | Eficacia y seguridad de mebendazol contra nitazoxanida en el tratamiento de Giardia lamblia en niños | 29 | 6 | 31 |
| 5 | Lizardi-Cervera et al.20 | 2006 | Prevalencia de hígado graso no alcohólico y síndrome metabólico en población asintomática | 26 | 6 | 48 |
| 6 | Delgado-Enciso et al.21 | 2001 | Mutación 677 T del gen MTHFR en adenomas y cáncer colorrectal en una muestra de la población del noreste de México | 26 | 5 | 45 |
| 7 | Martínez-Vázquez et al.22 | 2012 | Effect of antispasmodic agents, alone or in combination, in the treatment of Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Systematic review and meta-analysis | 25 | 14 | 69 |
| 8 | Belmonte-Montes et al.23 | 1999 | Fistulotomía vs fistulectomía. Valoracion ultrasonográfica de lesión al mecanismo de esfínter anal | 24 | 6 | 43 |
| 9 | Dhroove et al.24 | 2017 | Prevalencia de trastornos gastrointestinales funcionales en escolares mexicanos | 23 | 6 | 18 |
| 10 | Montaño Loza et al.25 | 2006 | Prevención de hiperamilasemia y pancreatitis posterior a la colangiopancreatografía retrógrada endoscópica con la administración rectal de indometacina | 22 | 4 | 26 |
| 11 | Carmona-Sánchez and Tostado-Fernández26 | 2005 | La prevalencia del uso de medicina alternativa y complementaria en pacientes con síndrome de intestino irritable, dispepsia funcional y enfermedad por reflujo gastroesofágico | 21 | 7 | 31 |
| 12 | Vera de León et al.27 | 2005 | Panorama epidemiológico y situacional de la hepatitis C en México | 21 | 3 | 34 |
| 13 | Schmulson et al.28 | 2010 | Prevalencia y caracterización de los subtipos de SII según los criterios de Roma III, en un estudio clínico, multicéntrico. Reporte del grupo mexicano de estudio para el SII | 20 | 5 | 17 |
| 14 | Garza-González et al.29 | 2003 | Papel de los polimorfismos de algunas citocinas en el cáncer gástrico en México | 18 | 9 | 26 |
| 15 | Ayala-Gaytán et al.30 | 1997 | Prevalencia de marcadores virales para hepatitis B, C y Virus de la Inmunodeficiencia Humana en donadores de sangre voluntarios en el Noroeste de México | 18 | 2 | 22 |
| 16 | Ayala-Gaytán et al.31 | 2004 | Ciclosporidiosis: Características clínicas y diagnósticas de un brote epidémico | 16 | 4 | 19 |
| 17 | Ladrón-de Guevara et al.32 | 2002 | Prevalencia y factores de riesgo para hepatitis C en donadores de sangre | 16 | 1 | 16 |
| 18 | Martínez-Guzmán and De la Rosa-Bayón33 | 1998 | Neoplasias y displasias de vesícula biliar y su relación con litiasis. Estudio clinicopatológico de casos y controles | 15 | 4 | 18 |
| 19 | Oñate-Ocaña et al.34 | 1999 | Factores pronósticos en 793 casos de cáncer gástrico en un centro de referencia oncológico | 15 | 3 | 19 |
| 20 | Cruz-Ruíz et al.35 | 2007 | Asociación de depresión y ansiedad en pacientes con síndrome de intestino irritable | 15 | 2 | 25 |
| 21 | Roesch-Dietlen et al.36 | 2006 | Frecuencia del hígado graso no alcohólico en un grupo de pacientes con síndrome metabólico estudiado en la ciudad de Veracruz | 15 | 2 | 18 |
| 22 | Morán et al.37 | 1997 | Efecto de la administración de fibra en la prevención de litiasis vesicular en obesos sometidos a dieta de reducción. Ensayo | 15 | 1 | 31 |
| 23 | Herrera-López et al.38 | 2010 | Capsaicin induction of esophageal symptoms in different phenotypes of gastroesophageal reflux disease | 15 | 1 | 17 |
| 24 | Ruiz-Margáin et al.39 | 2018 | Effect of a high-protein, high-fiber diet plus supplementation with branched-chain amino acids on the nutritional status of patients with cirrhosis | 14 | 6 | 26 |
| 25 | Vázquez-Frias et al.40 | 2015 | Perfil de citocinas proinflamatorias y antiinflamatorias en pacientes pediátricos con síndrome de intestino irritable | 14 | 6 | 17 |
| 26 | Novoa-Farías et al.41 | 2016 | Susceptibilidad de las bacterias aisladas de infecciones gastrointestinales agudas a la rifaximina y otros agentes antimicrobianos en México | 14 | 4 | 12 |
| 27 | Baccaro and Sánchez42 | 2009 | Determinación de la desnutrición hospitalaria: comparación entre la valoración global subjetiva y el índice de masa corporal | 14 | 3 | 10 |
| 28 | Bernal-Reyes et al.43 | 2000 | Prevalencia de la esteatohepatitis no alcohólica (EHNA). Estudio comparativo con diabéticos | 14 | 2 | 28 |
| 29 | Charúa Guindic et al.44 | 2004 | Desarterialización hemorroidaria guiada por Doppler. Una alternativa quirúrgica en el manejo de la enfermedad hemorroidaria | 14 | 1 | 28 |
| 30 | Méndez-Sánchez et al.45 | 2007 | Effect of Helicobacter pylori infection on gastric ghrelin expression and body weight | 13 | 5 | 14 |
| 31 | Bahena-Aponte et al.46 | 2010 | Utilidad de la goma de mascar para la resolución del íleo posoperatorio en resecciones de colon izquierdo | 13 | 4 | 15 |
| 32 | Dehesa-Violante et al.47 | 2007 | Prevalence of hepatitis C virus genotypes in Mexican patients | 13 | 3 | 31 |
| 33 | Güitrón Cantú et al.48 | 1999 | Estenosis esofágica benigna en pacientes lactantes y preescolares. Resultados de dilatación endoscópica | 13 | 1 | 18 |
| 34 | Mejía-León et al.49 | 2015 | Gradiente de riesgo genético HLA-DQ para diabetes tipo 1 y enfermedad celíaca en el noroeste de México | 12 | 5 | 15 |
| 35 | Bernal Reyes and Licona Solis50 | 1996 | Seroepidemiology of hepatitis E in the State of Hidalgo | 12 | 4 | 16 |
| 36 | Palacio-Rúa et al.51 | 2014 | Análisis genético en APC, KRAS y TP53 en pacientes con cáncer de estómago y colon | 12 | 4 | 15 |
| 37 | Gallo et al.52 | 1998 | Superioridad clínical del pantoprazol sobre la ranitidina en la curación de la esofagitis por reflujo grado II y III. Estudio prospectivo, doble ciego, doble placebo. Experiencia clínica mexicana | 12 | 4 | 12 |
| 38 | Mercado et al.53 | 2005 | Prevalencia de anticuerpos contra virus de hepatitis C y B en pacientes con lupus eritematoso sistémico | 12 | 4 | 11 |
| 39 | Bosques-Padilla et al.54 | 2011 | Epidemiología y características clínicas de la colitis ulcerosa crónica idiopática en el noreste de México | 12 | 3 | 20 |
| 40 | Zúñiga-Noriega et al.55 | 2007 | Polimorfismo C677 T del gen MTHFR y el riesgo al desarrollo de cáncer gástrico distal en una población mexicana | 11 | 7 | 14 |
| 41 | Valerio-Ureña et al.56 | 2010 | Prevalencia del síndrome de intestino irritable en población abierta de la ciudad de Veracruz, México | 11 | 3 | 22 |
| 42 | Gómez-Escudero et al.57 | 2004 | Utilidad diagnostica del cuestionario de Carlsson-Dent en la enfermedad por reflujo gastroesofágico (ERGE) | 11 | 2 | 25 |
| 43 | Gupta 58 | 2008 | Closed anal sphincter manipulation technique for chronic anal fissure | 11 | 2 | 18 |
| 44 | Duarte-Rojo et al.59 | 2009 | Liver transplantation for neurologic Wilson’s disease: reflections on two cases within a Mexican cohort | 11 | 2 | 14 |
| 45 | Schmulson Wasserman and Valdovinos Díaz60 | 1998 | Utilización de recursos médicos por los pacientes con síndrome de intestino irritable en un hospital de tercer nivel | 11 | 1 | 5 |
| 46 | García-Compean et al.61 | 2005 | Utilidad diagnóstica e impacto clínico de la cápsula endoscópica en la hemorragia gastrointestinal de origen oscuro | 11 | 0 | 12 |
| 47 | Mejía-Rivas et al.62 | 2009 | Gastric capacity is related to body mass index in obese patients. A study using the water load test. | 10 | 6 | 12 |
| 48 | Fonseca-Camarillo et al.63 | 2009 | Expresión del gen de IL-6 y TNF-α en la mucosa rectal de pacientes con colitis ulcerosa crónica idiopática y controles | 10 | 5 | 0 |
| 49 | Rojano-Rodríguez et al.64 | 2014 | Nivel de proteína C reactiva en pacientes con obesidad mórbida antes y después de cirugía bariátrica | 10 | 4 | 10 |
| 50 | Güitrón et al.65 | 1996 | Extracción de cuerpos extraños en el esófago. Experiencia en 215 casos | 10 | 3 | 29 |
GS: Google Scholar; PM: PubMed; S: Scopus.
The most relevant consensuses and review articles are described in Table 2, identifying the 10 most relevant works, with a total of 208 citations.
The most-cited consensuses and review articles in Spanish or English published in the Revista de Gastroenterología de México.
| Lead author | Year | Title | No. of citations | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | PM | GS | ||||
| 1 | Galicia-Moreno and Gutiérrez-Reyes66 | 2014 | The role of oxidative stress in the development of alcoholic liver disease | 48 | 24 | 63 |
| 2 | Schmulson et al.67 | 2014 | Microbiota, gastrointestinal infections, low-grade inflammation, and antibiotic therapy in irritable bowel syndrome: an evidence-based review | 28 | 11 | 50 |
| 3 | Icaza-Chávez68 | 2013 | Microbiota intestinal en la salud y la enfermedad | 27 | 7 | 51 |
| 4 | Bonilla and Saps69 | 2013 | Eventos en edad temprana predisponen al desarrollo de trastornos gastrointestinales funcionales | 25 | 9 | 45 |
| 5 | Yamamoto-Furusho et al.70 | 2017 | Situaciones especiales de la enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal: Primer Consenso Latinoamericano de la PanAmerican Crohn's and Colitis Organisation | 15 | 3 | 27 |
| 6 | Turumin et al.71 | 2013 | The role of the gallbladder in humans | 14 | 5 | 29 |
| 7 | Carrada-Bravo72 | 2003 | Fascioliasis. Diagnóstico, epidemiología y tratamientos | 14 | 2 | 20 |
| 8 | Porres-Aguilar et al.73 | 2013 | Complicaciones vasculares pulmonares en hipertensión pulmonar y enfermedades hepáticas: una revisión concisa | 14 | 2 | 1 |
| 9 | Takahashi et al.74 | 1994 | Evaluation and treatment of constipation | 12 | 4 | 23 |
| 10 | Valdovinos et al.75 | 2017 | Consenso mexicano sobre probióticos en gastroenterología | 11 | 3 | 23 |
GS: Google Scholar; PM: PubMed; S: Scopus.
The original article with the most citations was the 2004 study by Franklin et al.16 on the utility of laparoscopic right hemicolectomy in the colon cancer scenario, with 39 citations, followed by Zablah et al.17 (prevalence of functional gastrointestinal disorders, 34 citations), Hernández-Aranda et al.18 (refeeding syndrome, 33 citations), Rodríguez-Garcia et al.19 (treatment of Giardia lamblia, 29 citations), and Lizardi-Cervera et al.20 (prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and metabolic syndrome, 26 citations).
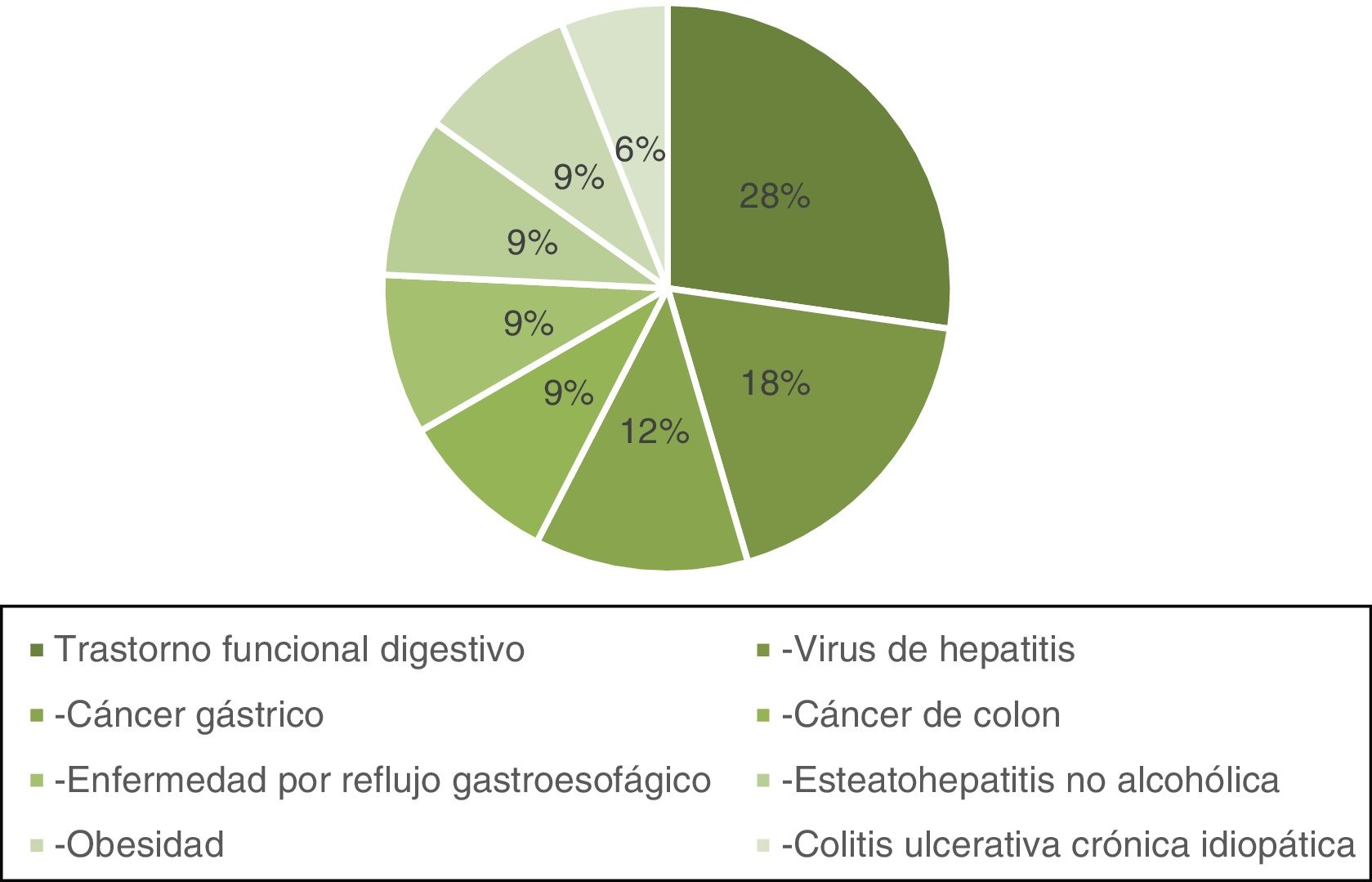
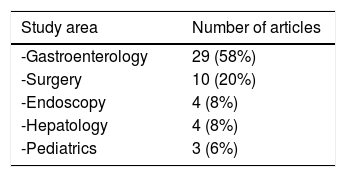
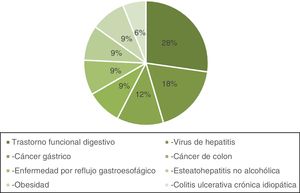
Fig. 1 shows the classification by topic of the original articles with the highest number of citations. The most frequent topic was functional gastrointestinal disorders (n = 9), followed by viral hepatitis (n = 6), and gastric cancer (n = 4). Less frequently viewed topics were colon cancer, gastroesophageal reflux disease, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, obesity, and ulcerative colitis (UC). The majority of the works were on general topics of gastroenterology (58%) and surgery (20%). Other areas covered were endoscopy, hepatology, and pediatrics (Table 3).
A total of 291 authors belonged to 120 institutions and the authors of the most-cited original works were from 7 countries. The healthcare institutions with the highest number of published works were the Instituto Mexicano del Seguro Social (IMSS) and the Instituto Nacional de Ciencias Médicas y Nutrición “Salvador Zubirán” (INCMNSZ), as shown in Table 4.
Institutions with greater number of original articles cited.
| Institution | Number of articles |
|---|---|
| -Instituto Mexicano del Seguro Social (IMSS) | 19 |
| -Instituto Nacional de Ciencias Médicas y Nutrición “Salvador Zubirán” (INCMNSZ) | 10 |
| -Hospital Universitario “Dr. José Eleuterio González” (UANL) | 8 |
| -Fundación Clínica Médica Sur | 4 |
| -Hospital General de México | 4 |
| -Instituto de Seguridad y Servicios Sociales de los Trabajadores del Estado (ISSSTE) | 4 |
| -Hospital Manuel Gea González | 3 |
| -Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México (UNAM) | 3 |
| -Centro Médico ABC | 2 |
Thirty-six percent of the most-cited original articles were studies with a nonrandomized prospective design, followed by cross-sectional studies (26%) and randomized prospective studies (18%). Sixty-five percent of the studies had levels of evidence III and IV and 22% had levels of evidence I and II.
Table 5 describes the most widely read articles of the RGM, which includes articles with more than 2 million views.
The 10 most-viewed articles in both Spanish and English published in the Revista de Gastroenterología de México and alternative metrics.
| Lead author | Year | Title | Alternative metrics* | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total number of views (PDF, HTML, EPUB) | Citations(Scopus, CrossRef) | Usage | Captures | Social media | ||||
| 1 | Remes-Troche et al.76 | 2010 | Pharmacological treatment of the irritable bowel syndrome: a technical review | 765,630 | 4 | – | – | – |
| 2 | Sierra et al.77 | 2014 | Ideal treatment for Helicobacter pylori: a systematic review | 592,971 | 7 | 35 | 173 | 2 |
| 3 | Arismendi-Morillo et al.78 | 2013 | Gastric cancer risk estimate in patients with chronic gastritis associated with Helicobacter pylori infection in a clinical setting | 330,152 | 4 | 107 | 116 | 6 |
| 4 | Icaza-Chávez79 | 2013 | Gut microbiota in health and disease | 212,626 | 31 | 80 | 1,374 | 257 |
| 5 | Huerta-Iga et al.80 | 2016 | Diagnosis and treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease: recommendations of the Asociación Mexicana de Gastroenterología | 183,140 | 6 | 716 | 461 | 7 |
| 6 | Remes-Troche et al.81 | 2010 | Diagnosis and treatment guideline of chronic diarrhea | 168,885 | 0 | – | – | – |
| 7 | Torre-Delgadillo et al.82 | 2009 | Gastroenterology diagnosis and treatment guidelines of hepatic encephalopathy. Treatment and future prospects | 166,010 | 1 | – | – | – |
| 8 | Yamamoto-Furusho et al.83 | 2017 | Diagnosis and treatment of inflammatory bowel disease: First Latin American Consensus of the Pan American Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation | 153,984 | 16 | 1,416 | 270 | 24 |
| 9 | Narváez-Rivera et al.84 | 2013 | Mexican Consensus on Portal Hypertension | 147,553 | 5 | 42 | 310 | – |
| 10 | Moctezuma-Velázquez85 | 2018 | Current treatment for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease | 134,341 | 3 | 155 | 197 | 62 |
In the present study, we identified the most-cited original articles, review articles, and consensuses of greater impact published in the official journal of the Asociación Mexicana de Gastroenterología, the RGM. The shared characteristics of the articles were identified and analyzed, together with their relation to the number of citations. Said analysis is an acknowledgement of the researchers and institutions that have contributed to the Mexican medical literature through original works and up-to-date information in the field of gastroenterology and its related areas.
The role of bibliometrics in evaluating the quality of scientific literature has been debated in recent years. A directly proportional relation between the perception of the success of an article and the number of citations87 has been reported in reviews, whether due to the originality of the information at the time of its publication or to the conversion into a “dogmatic” status of works within a certain area of study. Nevertheless, it is important to keep in mind that the number of citations of an article is a surrogate measure of the relevance and relative impact of said article in the scientific literature.88,89 Therefore, the number of citations, alone, cannot substitute other measures of quality in research, such as peer review.90
The most-cited article was the case series of laparoscopic right hemicolectomies by Franklin et al.,16 at the Texas Endosurgery Institute. It is a prospective study spanning 11 years (1991-2002) on the oncologic and nononcologic utility of laparoscopy, suggesting noninferiority, when compared with the open technique. The first laparoscopic resection of the colon was simultaneously reported in 1991 by Jacobs et al.91 in Miami and Fowler and White92 in Kansas. In the 1990s, the oncologic utility of laparoscopic colectomies was a subject of discussion, and the team of Franklin et al.16 were pioneers in the field.93 The mediatic impact of their article and its success can be understood in that context, which is highlighted by the presence of a world class study in a Mexican journal.
The RGM dates back to 1935, but the most-cited original articles correspond to the period between 1996 and 2018, which is most likely associated with greater access to scientific literature, thanks to the Internet and the increase in the number of scientific journals worldwide. The years in which there was a larger number of highly cited articles were 1999, 2004, 2005, 2007, 2009, and 2010, with four articles per year, respectively. Over time, a change in the focus of the topics studied can be observed, beginning with a search for risk factors and then moving to the study of biochemical or molecular markers or clinical outcomes.
The IMSS was the institution with the highest number of publications. That result could involve bias associated with the multicenter nature and structure of the Mexican healthcare system. Nevertheless, the IMSS, together with the INCMNSZ and the Hospital Universitario “Dr. Eleuterio González” of the Universidad Autónoma de Nuevo León (UANL), are the institutions with a relevant number of members associated with the National System of Researchers.94
With respect to the study designs, the majority of the works were quasi-experimental studies, i.e., nonrandomized prospective studies, followed by cross-sectional and randomized prospective studies. Interestingly, 65% of the works had evidence levels III and IV, reflecting the fact that a study does not require level I or level II evidence to significantly impact the scientific literature.
In addition, the interaction of the medical community with digital media, as well as their increased use in recent years, can be observed through different alternative metrics. Scientific studies have had greater reach, resulting from the use of the Internet and social media.
ConclusionThe present review provides an overview of the most highly cited original works published in the RGM. The 50 most-cited articles account for a total of 826 citations and the 10 most-cited consensuses and review articles account for 208 citations. Those works present diversity in disciplines related to gastroenterology and reflect the work of different active research groups in Mexico and other countries. The original articles described herein are the recipients of 20% of all the citations from the RGM, demonstrating the importance and impact they have had on the scientific community.
Ethical considerationsNo patients participated in the present study, nor were patient data utilized, and so obtaining informed consent was not necessary. Likewise, given that there were no interventions, maneuvers, or information management involved, the study was considered a low-risk analysis and required no review or approval by the local ethics committee. Even so, the study meets the current research regulations and the confidentiality of personal and identification data, as well as the anonymity of the participants (all healthcare workers that participated voluntarily) are guaranteed. The present article contains no personal information that could identify the participants.
Financial disclosureNo financial support was received in relation to this article.
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Please cite this article as: Sánchez-Morales GE, Rojas-Gutiérrez E, González-Martínez CA, Bonilla-Salas A, Yamamoto-Furusho JK, Los artículos más citados en la Revista de astroenterología de México en un período de 22 años (1996-2018), Revista de Gastroenterología de México. 2021;86:59–69.