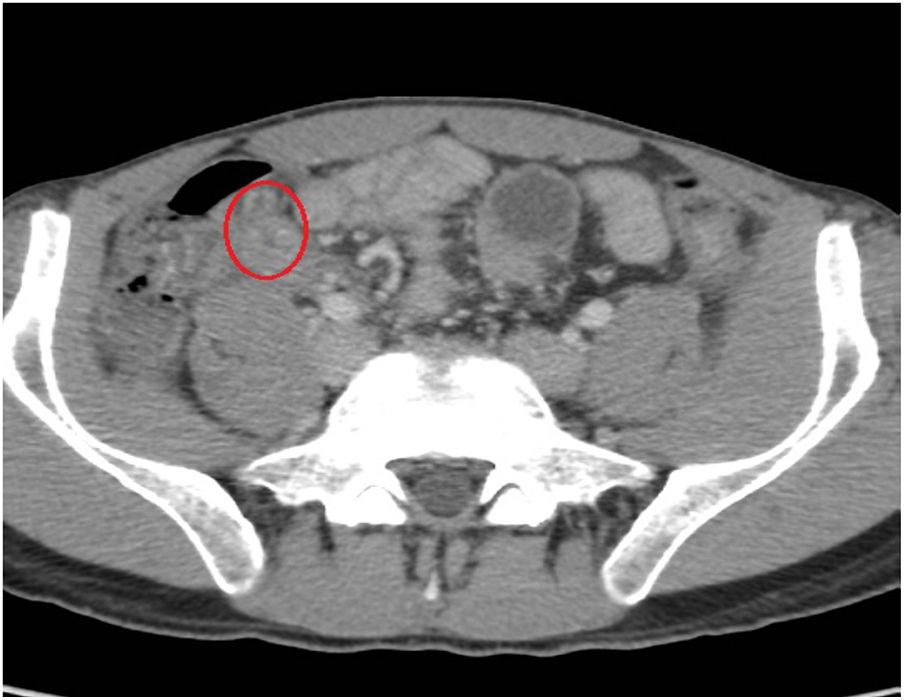
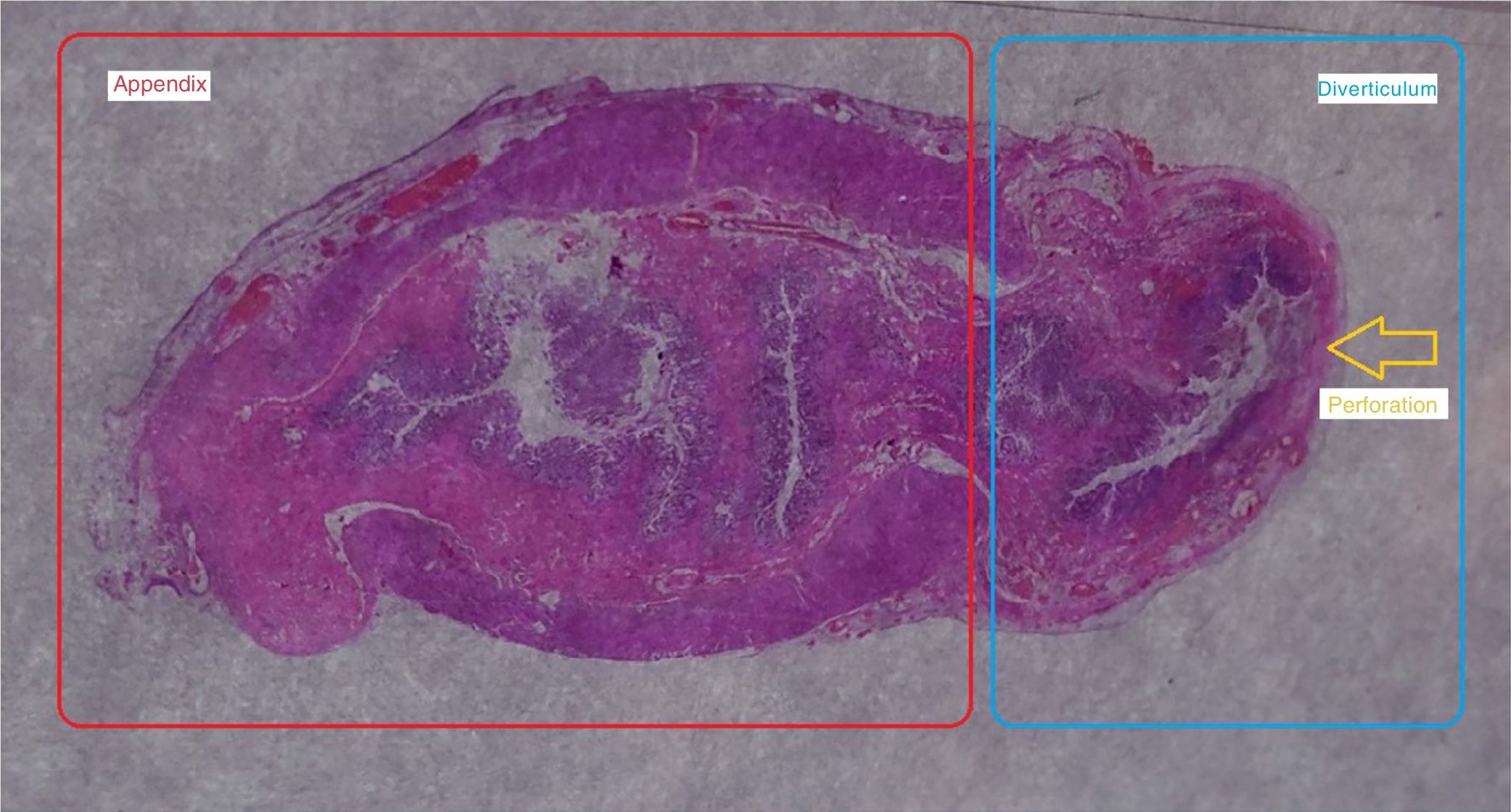
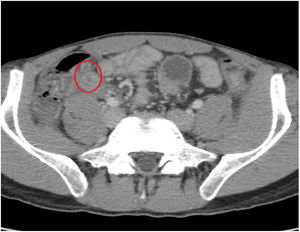
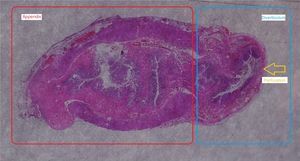
A 27-year-old man came to the emergency room due to 24h epigastric abdominal pain radiating to the right iliac fossa. Upon physical examination, the Blumberg sign was positive and laboratory test results showed leukocytosis with neutrophilia. An abdominal CT scan revealed a post-ileal appendix with thickened walls in which small diverticula were identified (fig. 1, red circle). There were inflammatory changes and a small quantity of fluid in the periappendiceal fat, alterations consistent with appendiceal diverticulitis associated with acute appendicitis. Appendectomy was performed and multiple diverticula, with microperforation in the proximal third of one of them (fig. 2, yellow arrow), were confirmed in the anatomopathologic study. Appendiceal diverticulitis is an uncommon cause of acute abdomen and is clinically indistinguishable from acute appendicitis. On occasion it can be differentiated due to a more indolent course and certain aspects of its epidemiology and progression. Although CT images can be very suggestive of the pathology, the definitive diagnosis is made through histologic study of the surgical specimen in the majority of cases.
Ethical disclosuresProtection of human and animal subjectsThe authors declare that the procedures followed were in accordance with the regulations of the relevant clinical research ethics committee and with those of the Code of Ethics of the World Medical Association (Declaration of Helsinki).
Confidentiality of dataThe authors declare that patient data has been handled confidentially and anonymously, following the protocols of their work center.
Right to privacy and informed consentThe authors have followed the protocols of their work center in relation to the publication of patient data, maintaining their confidentiality and anonymity.
Financial disclosureNo financial support was received in relation to this study/article.
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Please cite this article as: Arenas-García V, Santos-Seoane SM, Delgado-Sevillano RJ. Diverticulitis apendicular: una causa infrecuente de abdomen agudo. Revista de Gastroenterología de México. 2019;84:243–244.