Enteric duplication cysts are a rare finding in the population, and when appearing in the pancreas, are called pancreatic duplication cysts. They present as acute pancreatitis, which can be severe, or as recurrent abdominal pain.
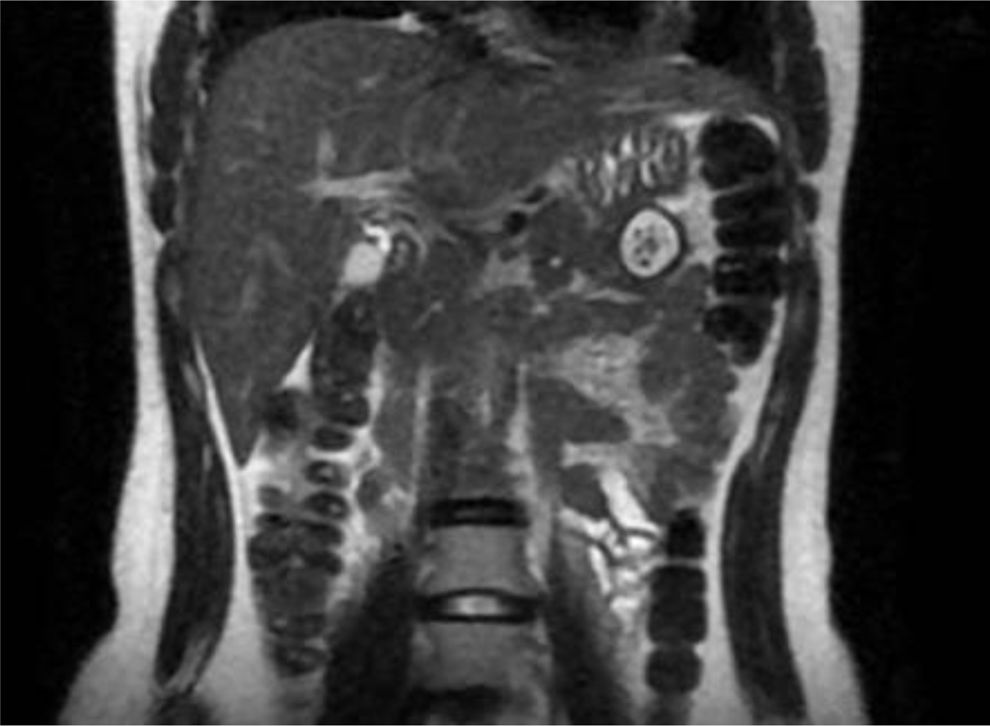
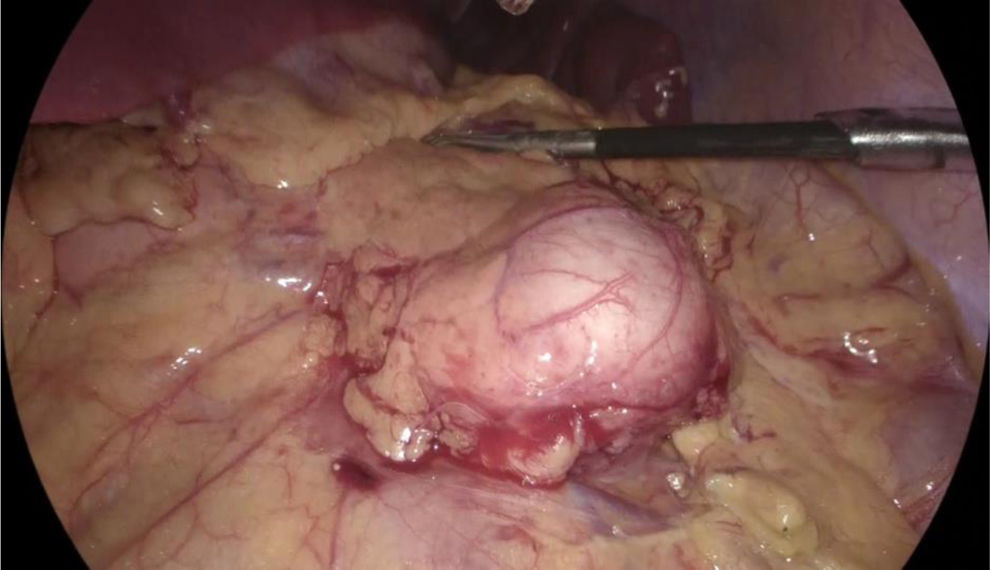
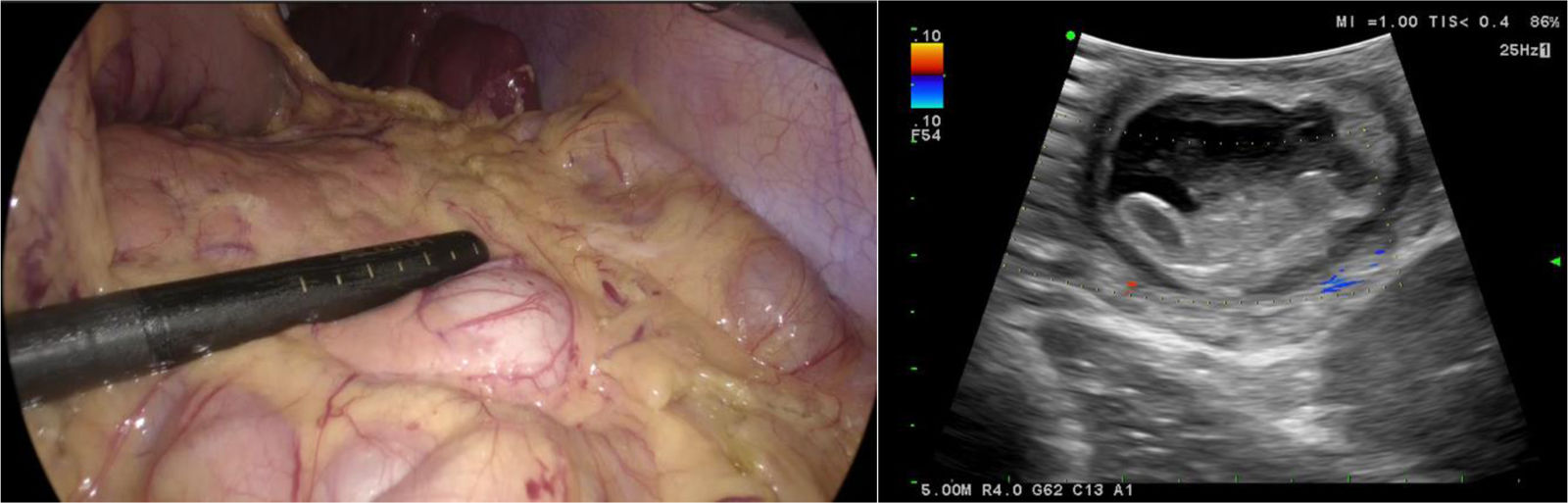
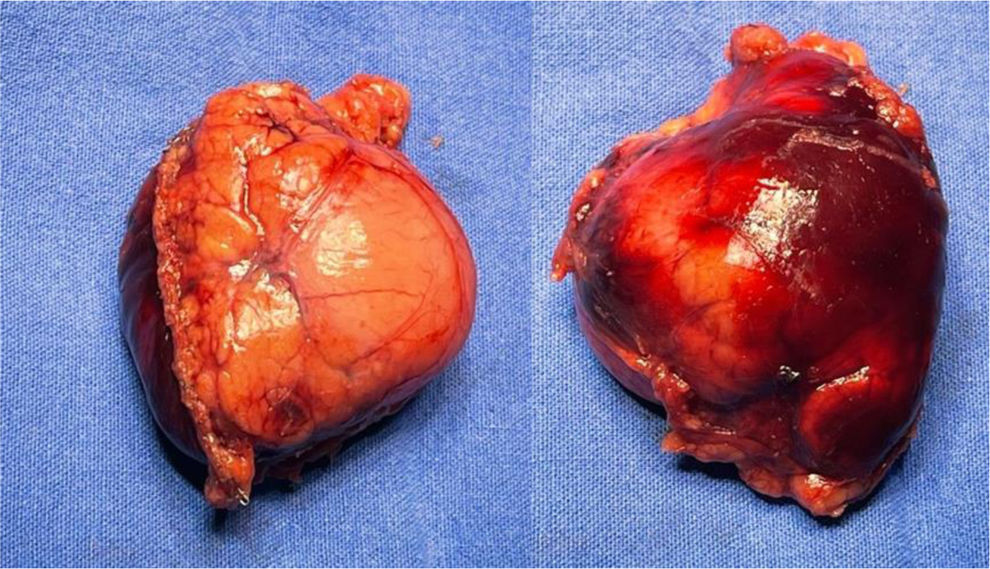
A 19-year-old woman came to the emergency room due to experiencing sharp, burning, nonradiating abdominal pain (NRS 8/10) in the hypogastrium for 24 h, with no accompanying symptoms. A computed tomography (CT) scan identified a cystic lesion in the pancreas. To determine its origin, a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan with contrast was carried out, revealing a “fish-tail pancreas”. The cystic lesion measured 2.7 cm, with thick (3 mm), well-defined walls and post-contrast enhancement, leading to the suspicion of pancreatic duplication cyst (Fig. 1). The patient underwent laparoscopy (Fig. 2), and an intraoperative ultrasound with a multifrequency phase selection laparoscopic transducer was carried out, identifying an anechoic structure with regular edges that was dependent on the pancreatic parenchyma, as well as a negative Doppler shift. The sonographic layer was similar to that of the intestinal wall (Fig. 3). The cyst was resected utilizing an Echelon stapler (Fig. 4). The patient was released with no complications and remains under surveillance by our service, with good progression.
Intraoperative ultrasound showing an anechoic lesion with regular edges and negative Doppler shift. The sonographic layer of the wall is similar to that of the intestinal wall and there are no signs of vascular invasion or invasion into the adjacent parenchyma. The data are consistent with pancreatic duplication cyst.
The authors declare that the patient signed a written statement of informed consent for the publication of this article, in accordance with the policies and norms of the committee on ethics and research on humans at our institution. The present article contains no personal information that could identify the patient. No experiments were conducted on animals or humans.
Financial disclosureNo financial support was received in relation to this article.
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.